Globe's Radial Piston Air Motors assemblies comply with ATEX standards by utilising key features within the brake system. This system ensures that the brake operates seamlessly with the motor, maintaining safety and performance standards. In this overview, we delve into the brake mechanism, connection setups, and maintenance considerations for ATEX compliance.
The Operating Principle of the Brake
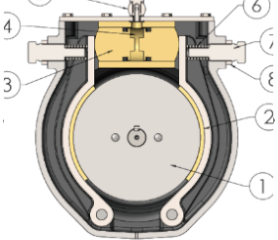
The brake is designed with a corresponding mounting interface, allowing direct attachment to the motor. It consists of two spring-applied brake shoes, denoted as (2), which exert pressure on a central hub (1). This hub is mounted on the output shaft of the motor. These brake shoes are released by applying air pressure to the cylinder/piston assembly (3/4). Notably, the brake torque can be adjusted via two spring adjusters (7). However, in ATEX applications, GLOBE pre-sets the brake to a maximum torque that aligns with the motor's operating pressure. Unauthorised adjustments to this setting will compromise ATEX compliance. Likewise, any modifications to the pneumatic system, including the valves controlling the brake, will render the ATEX certification invalid.
Ensuring Proper Brake Integration
To ensure the successful integration of the brake system, the brake must be mounted to a GLOBE Piston motor of the equivalent size. For example, the RM110 Brake (112-900) should be paired with the RM110 Motor (R14XXXA00). This includes the correct piping and control valves, which are provided by GLOBE / MacScott Bond.
The end-user should communicate the maximum operating pressure of the motor to MacScott Bond / Globe. To adhere to ATEX requirements, the required pressure for releasing the brake is set by GLOBE / MacScott Bond. This is achieved by adjusting the GLOBE APPV3214 valve, which is now integrated into the pneumatic control system. When the system's pressure drops below 20% of the set release pressure, the valve will close, preventing any inadvertent brake dragging or mishandling.
Specific Conditions for ATEX Compliance
ATEX compliance is contingent on avoiding any scenario where the brake drags while the motor is in operation. Such dragging can lead to friction and heat generation within the brake. The pilot pressure that releases the brake is pre-set in the factory and must always be equal to or higher than the motor's inlet pressure. This setting not only ensures the brake's release but also establishes the maximum motor inlet pressure, which corresponds to the required brake holding torque for the associated piston motor. Therefore, the customer must provide their desired working pressure (pressure threshold) before delivery, which is set in a specialised valve, the GLOBE APPV3214, which controls the brake.
Warning
The brake is NOT equipped with a locking device. The braking force is based on
friction and is caused by a friction material which is pushed against the braking
wheel and brake housing. When the load is higher than the rated holding torque
the brake will slip and the load can not be held.
Connection Setups
The motor and brake assembly can be categorised into three operational setups (1, 2, and 3), each offering two different connection methods (A and B). These setups are as follows:
- Setup 1A: Direct connection between the motor and the air line, with the brake control system operated by the motor inlet pressure.
- Setup 1B: Direct connection between the motor and the air line, with the brake control system operated by an external pressure source.
- Setup 2A: Motor operated by a Hand Control Valve (HCV), with the brake control system operated by the motor inlet pressure.
- Setup 2B: Motor operated by an HCV, with the brake control system operated by an external pressure source.
- Setup 3A: Motor operated by a Remote Control Valve (RCV), with the brake control system operated by the motor inlet pressure. The RCV can be controlled by another valve via pilot ports.
- Setup 3B: Motor operated by an RCV, with the brake control system operated by an external pressure source. The RCV can be controlled by another valve via pilot ports.
Understanding the ATEX-certified GLOBE Piston Motor Brake is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance in environments with explosive atmospheres. With detailed insights into the brake's operation, connection setups, and maintenance procedures, users can confidently operate and maintain this component while adhering to ATEX standards.
Please remember that unauthorised adjustments or modifications to the brake system can jeopardise ATEX certification and safety standards. Always follow the recommended procedures and guidelines for safe and compliant operation. If you have any questions or need further assistance, please do not hesitate to contact us. Your safety and compliance are our top priorities.